Who should submit annual reports and statutory audits?
According to the Company Law of the People’s Republic of China, all companies registered in China, including limited liability companies, joint stock limited companies, non corporate entities, and other commercial entities, are required to undergo an annual inspection in order to continue operating in the following year. The purpose of annual inspection is for the Administration for Industry and Commerce to review and confirm the eligibility of enterprises to continue operating annually.
With the development and implementation of China’s social credit system, compliance with laws and regulations has become more important than ever before. More attention should be paid to the annual compliance procedures stipulated by various government departments.
Here, we will introduce to you the annual compliance requirements for wholly foreign-owned enterprises or Chinese representative offices.
What is the difference between annual tax settlement and annual report?
Annual tax settlement refers to the consolidation of taxable income and already paid taxes for the previous accounting year by an enterprise to determine whether additional taxes need to be paid or apply for tax refunds. After filling out the annual corporate income tax declaration form, the company can submit the required information to the local tax bureau for corporate income tax declaration and tax settlement. The final settlement report of income tax will be completed by the bookkeeping agency, accounting firm or tax accounting firm and submitted to the tax bureau.
For annual reports, companies registered before the end of the calendar year should demonstrate their ability to continue operating in the following year by providing materials that meet the requirements of joint inspections with various government departments. The report will be submitted to the Administration for Industry and Commerce, which is another department, not the tax bureau.
Important dates to remember!
According to Article 4 of the Enterprise Annual Inspection Measures, the start and end dates of the annual inspection are from March 1st to June 30th each year. The registration authority shall inspect the situation of the enterprise in the previous year within the prescribed time. Enterprises shall submit annual inspection materials to the registration authority before March 15th.
In addition, when conducting business in China, you should remember three important dates before which you need to complete the corporate income tax/personal income tax declaration and submit the annual report. Otherwise, it may result in punishment and have a negative impact on the company’s credit.
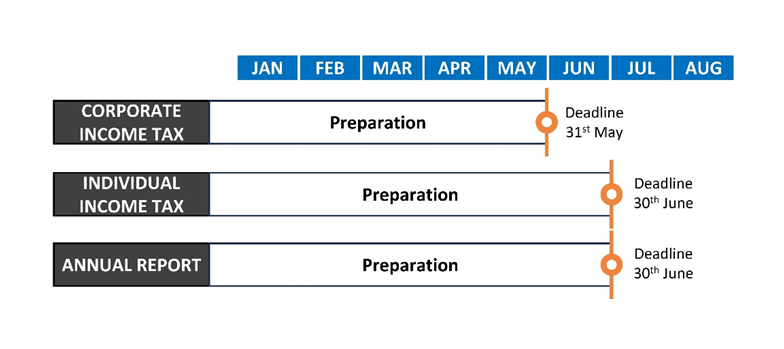
Annual compliance requirements for foreign-invested enterprises (wholly foreign-owned enterprises and joint ventures)
The annual compliance requirements begin after the end of the fiscal year (December 31st, which follows the calendar year in China), and typically last until the end of June for wholly foreign-owned enterprises and joint ventures.
Step 1: Prepare the annual audit report
The company’s annual maintenance program begins with the preparation of an annual audit report, which can be prepared as early as November or December. However, due to the need to include data from the previous year, it is recommended to complete the audit report by the end of April and then file the annual tax declaration in May.
According to the requirements of the Company Law, the company needs to hire a Certified Public Accountant (CPA) to conduct a third-party annual audit. The annual audit report typically includes a balance sheet, cash flow statement, income statement, as well as records of changes in equity and supplementary financial statements. It is recommended to conduct an annual audit of the financial statements to ensure that the company’s financial statements comply with Chinese Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) standards. This also gives you the opportunity to check the financial and health status of the company.
The deadline for submitting the annual report is June 30th. Failure to submit the annual report may result in your company being included in the list of abnormal operations by the State Administration for Industry and Commerce. If a company fails to submit annual reports for three consecutive years, in the worst case scenario, its business license may be revoked. The administrative department for industry and commerce may conduct spot checks on the content of the company’s annual report announcement. If it is found through inspection that the company’s annual report conceals the true situation and engages in fraud, the administrative department for industry and commerce will impose penalties in accordance with the law, and inform relevant departments and bureaus, including public security, finance, customs, taxation, etc., of the information and identity of the legal representative and management personnel, resulting in a situation of “one violation, one punishment”.
Step 2: Perform Corporate Income Tax (CIT) Reconciliation
After preparing the annual audit report, the next step is to perform annual CIT reconciliation or annual CIT filing. In China, CIT payments are made on a monthly or quarterly basis, and companies are required to submit CIT declaration forms within 15 days after the end of each month or quarter.
In addition, the State Administration of Taxation requires companies to conduct annual CIT reconciliation within five months after the end of each year, provided that all tax obligations have been fulfilled. However, in some cases, these companies are required to pay additional taxes or apply for tax refunds.
The annual CIT reconciliation needs to be completed before May 31st each year. However, the investigation into tax compliance may last for a year, and if requested by the tax bureau, the company should be prepared to submit additional materials at any time.
Step 3: Company Annual Report Procedure
After completing the first two steps, the next step is to submit annual reports to multiple administrative departments before the deadline of June 30th. Starting from 2020, companies can submit their annual reports through the National Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt. gov.cn), eliminating the need to report separately to different departments. A general report should include the following information:
- Implementation and modification of enterprise registration information
- The investment or cooperation conditions provided by shareholders or investors
- The investment conditions and background of the enterprise
- Establishment of branch offices or other organizations by enterprises
- Production and operation situation of the enterprise
Annual compliance requirements for Representative Office (RO)
The annual compliance procedures of RO are very similar to those of wholly foreign-owned enterprises and joint ventures. However, there may still be different needs and concerns in this process.
Step 1: Prepare the annual audit report
The audit report should be issued by a third-party accounting firm and signed by two certified public accountants, which is a mandatory requirement for certified public accountants. The report should include the following detailed information to distinguish it from wholly foreign-owned enterprises and joint ventures:
- Cost and expense reporting: The historical records of office rental, transportation, telephone expense reimbursement, employee salaries, hospitality expenses, utilities, and dispatch service fees should be carefully and accurately recorded, regardless of whether these expenses are paid by the RO itself or directly by its headquarters. Any expenses belonging to the accounting year should be appropriately provisioned and supported by contracts or agreements. The total salary of the chief representative, whether paid overseas or locally, must be included in the expenses.
- Tax payable: According to relevant laws and regulations, ROs of foreign enterprises in Chinese Mainland must pay corporate income tax on their recognized taxable income. According to the cost plus method, the taxable income, which is considered as income e, is calculated based on expenses. The recognized profit margin shall be determined by the tax bureau and shall not be lower than 15%;
Step 2: Conduct annual tax reconciliation
Like wholly foreign-owned enterprises and joint ventures, RO also needs to declare annual taxes to the local tax bureau before the end of May each year. If the audited payable tax differs from the tax paid by the responsible person, the responsible person should discuss the changes with the tax bureau. In this case, you can schedule a meeting with Simon’s tax advisor to discuss the reasons for the differences.
Step 3: Company Annual Report Procedure
The focus of the annual report of ROs is to showcase the legal status and status of the overseas headquarters SR for approval. Information related to business activities should also be added. The RO report checklist is as follows:
- Annual report
- Business Registration Certificate
- Audit report
- Prove the legal status and status of the overseas headquarters
Why choose Simon?
Rapid Processing
With experienced team members, we can handle your project faster than others.
Unsuccessful, no charge
Simon promises that we will only charge after your project is successfully completed.
Tailored services
We will provide the most suitable business plan based on your situation.
Traceable process
Simon has an online system for you to track any updates to the project.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do you have any further questions? don’t worry! We are happy to answer!
Why is annual maintenance important for Chinese companies?
Annual maintenance is crucial for Chinese companies to maintain competitiveness, compliance, and adaptability in a dynamic business environment. It helps identify operational inefficiencies, legal compliance gaps, and strategic opportunities that contribute to the long-term success of the company.
Which regions of Chinese companies should undergo annual maintenance?
The key areas that Chinese companies should conduct annual maintenance in include:
- Financial statements and accounting records
- Tax planning and compliance
Depending on the industry category in which your company operates, other specific requirements for other factors may include:
- Legal documents and contracts
- Human Resources Policies and Procedures
- IT systems and network security measures
- Physical infrastructure and equipment
- Marketing and Business Development Strategy
Can I handle annual maintenance tasks internally?
Yes, many maintenance tasks can be handled internally. However, for tasks that require specialized knowledge (such as legal compliance, tax planning), it is recommended to involve professionals familiar with Chinese regulations and business practices.
Will the annual maintenance cost be significant for a Chinese company?
The cost may vary due to the complexity of operations, the need for professional services, and any necessary system upgrades. However, these costs are investments in the long-term sustainability of the company. Collaborating with third-party service providers can help you save on budget by outsourcing reports to professionals such as Simon.
What would happen if I neglect the annual maintenance of my Chinese company?
Undoubtedly, skipping the annual maintenance and inspection required by law will result in administrative penalties such as fines. In addition, this will also have a negative impact on your own company. Neglecting annual maintenance may lead to financial, legal, and operational risks. This may result in missing regulatory compliance deadlines, inefficient operations, lost opportunities, and potential legal liabilities.
